Anonymous access on the Internet. Overview of ways to stay anonymous online
01/29/17 3.9KIn this article we will talk about all aspects related to anonymity on the Internet so you can maintain your privacy while browsing the Internet:
We're not saying that you can become completely anonymous, that's practically impossible. But what we can actually do is try to make online interactions more hidden.
Stay incognito
Private browsing mode or incognito mode is a feature that is the second most popular browsing option in browsers. It is quite suitable for those cases when you access the Internet from someone else's computer and want to check your Facebook, Twitter or email accounts.Likewise, it is ideal for testing sites that are heavily loaded with cookies. And also for those cases when the computer you are working on has public access.
Private browsing does not completely erase your fingerprints. Certain items, such as DNS lookups and some cookies, may remain after the session. So it's better to consider programs for anonymity on the Internet as a temporary measure. The main thing I want to draw your attention to is do not save your browsing history on a public computer.
If you want the best example, then open a private browsing session and browse a few sites, then exit the session, go to command line and enter the following:
Ipconfig/displaydns and press Enter.
This will be a list of all cached DNS entries visited from your computer, regardless of whether you used a private browsing session or not.
To delete entries, enter the following command:
Ipconfig/flushdns and press Enter.
This will clear the list and prevent any attempts to access it. It is also advisable to configure batch file, which will launch the browser in private browsing mode and automatically clear it when closed DNS records. This method can be used to maintain a certain level of privacy.
False identity
Using a fake identity sounds more intriguing than it actually is, but in many cases it is quite effective for achieving anonymity on the Internet:
Consider this example: you use the address Email to login to Facebook, Twitter, eBay and online games. This may seem quite reasonable, but for the hacker the task is now much easier. He only needs to hack one account or track you. But if you had many aliases, it would take a hacker much more time and effort to track down all the fake identities and identify the real user.
It's a simple concept, but it can be used to great effect to disguise your online activity. There have been cases where people have used over fifty fake names and email addresses to log into websites to avoid identifying their real identity.
There are few reasons to provide your real identity online. Most sites only collect and sell your data, or use it for advertising purposes, so under no circumstances provide your real email address, home address, or contact information on public sites:
If using fake identities is a hassle and you need something like a fake identity generator, you'll find it here.
How to maintain anonymity on the Internet? This site can completely create a fake identity with names, addresses, email addresses and phone numbers. He may even provide you with a number of fake credit cards, mother's maiden name, vehicle, blood type, height, weight and QR code, which can be used on not very reliable sites. It is obvious that all data provided is fake and any resemblance to real person is random.
The fake name generator also creates a fake email address that is working and you can use it to receive one-time email verification links. However, you cannot be sure who is also using this service. Nobody knows who else has access to this system. So it's better to think of it as a tool for generating email addresses that can be used to fill out various online forms.
Tools that help you stay invisible
Exists whole line programs with which you can hide your actions, erase your digital fingerprints, or remain invisible on the Internet. The most famous of them is the Tor Network. But those who require a higher level of encryption and anonymity may want to consider using a VPN ( Virtual Private Network).
Tor Network
Tor is program for anonymity on the Internet in Russian, with which your online connections are passed through connected networks, each owned by volunteers from around the world. The essence of this concept is to block the ability to track a user and find out his location, and give you the opportunity to visit blocked sites:
Tor Browser Bundle is a free package for Windows, Mac and Linux that, when launched, automatically connects you to the Tor Network and also launches a specially designed and modified version of Firefox.
Once the package is launched, when you start browsing sites through Tor, all content you connect to is transferred encrypted and passed through the network system mentioned above. Tor Browser Bundle works effectively with any TCP instant messaging, remote login, and other browser applications. However, this product does not guarantee 100% anonymity and should not be used to download illegal music or movies. This may cause overload in Tor networks and cause problems for users who use the package for proper purposes.
The protocols used by P2P sites can often be used to scan an IP address, and will allow you to figure out your actual IP address, not the one generated by Tor.
However, Tor is a great product that you can use to stay anonymous. Built-in Firefox version, based on Extended Support Release ( ESR) Firefox by Mozilla, specially modified to optimize security and privacy features. To achieve this, access to the Components.interfaces element, which can be used to identify the user's computer platform, was blocked. With the exception of some Flash add-ons, caching of SSL sessions is prohibited and DNS information leakage via WebSockets is blocked.
By using the Tor Browser Bundle, you will be relatively protected from online snooping ( except for the most cunning attackers). Although ensure complete anonymity on the Internet you won't be able to:
If you look at the above screenshot, you will see that by navigating through Tor, your IP address is hidden. This is achieved by disabling JavaScript. Besides modified version browser has successfully blocked the scripts needed to collect information about your system.
If you'd like to try the Tor Browser Bundle and see how well it does at hiding your digital fingerprints, head over to the Tor website where you can download the bundle itself. And also get more information about how Tor helps you achieve anonymity and security when working on the Internet.
HMA VPN
This is an impressive VPN service from the UK that allows the user to hide their IP addresses, unblock some sites, geo-restricted channels and anonymously visit sites through one of the company's over 50 thousand private and anonymous IP addresses:
HMA's 934 VPN servers are located in 190 countries, using OpenVPN, PPTP and L2TP protocols. It is useful and easy to use software. All you have to do is subscribe to one of tariff plans: £7.99 for one month, £5.99 per month for six months or £4.99 per month for a year. After this, you need to install the software, enter your username and password and connect to the service.
All the hard work and configuration VPN for online anonymity Internet is provided automatically. In addition, a special built-in function “ Speed Guide" will automatically select the fastest VPN server based on your current location and connection.
The software is available for Windows, Mac and Linux. After you have registered an account and paid for the selected tariff plan, you can download necessary software via HMA control panel:
Manager software The VPN includes some interesting features, one of which is the connection speed review. You can also choose which VPN protocol you want to use. One of the most popular and fastest protocols is OpenVPN. In addition, you can set the parameters to change the IP address randomly every few minutes.
The program contains a convenient function " Secure IP Bind", which prevents applications from connecting to the Internet when HMA VPN is not running. You can choose your own country-specific VPN server and adjust the load ratio to connect to the VPN server with the fewest users and get more resources at your disposal.
CyberGhost
VPN, which is rightfully considered one of the best methods of anonymity on the Internet. CyberGhost 5.5 was recently introduced, which includes a number of additional benefits available in the paid package. Hiding your IP address and encrypting your connection is the norm for the CyberGhost team, but they feel they can do even more for you:
New features include Ad-Blocker, malware and virus protection, data compression, tracking prevention, force HTTPS functionality, and access through the fastest servers.
The data compression feature increases the speed of your mobile connection, and also identifies and actively removes any content that helps collect information about the resources you visit.
Forced transition to HTTPS is useful function which many VPNs don't implement. By forcing a secure connection, you increase security of your work on the Internet and reduce the risk of your data being stolen:
In addition to new features, CyberGhost 5.5 features a faster and more user-friendly interface. Connections to servers located outside the UK are faster and overall download speeds are faster. The service also provides handy graphs that show how many cases of blocking, tracking, and forced switching to HTTPS occurred while using CyberGhost.
For more information about how to maintain anonymity on the Internet and the cost of various plans, visit the CyberGhost website.
Browser Add-ons
If reducing traffic isn't a big concern for you and you're only concerned about snooping, then use one of the many free add-ons available for IE, Chrome, and Firefox.
They can help block certain scripts and pop-ups, as well as identify elements that track your location.
DoNotTrackMe/Blur
Recently released, but already widely known, improved version of DoNotTrackPlus. Compared with previous versions Over 300 advertising platforms have been added to its blacklist, as well as more than 650 tracking technologies:
The add-on is available for Chrome, IE, Safari and Firefox. Once you install the extension and restart your browser, the DNTMe icon will appear in your toolbar and DoNotTrackMe will begin logging attempts to track your activity.
DNTMe works great in parallel with already installed add-ons. Your browsing experience will not be slowed down, and you will see the same content as before, except for some of the ad elements that are being tracked. You will receive information about the number of attempts made and blocked.
Adblock Plus
Another free add-on for IE, Chrome and Firefox. It is considered one of the best for ensuring anonymity on the Internet, blocks phishing and tracking, and protects you from malware and unwanted advertising:
You can add ready-made filters or use custom ones. But be careful when using unknown filter lists, as they may miss something important.
NoScript
Extension for Firefox, Seamonkey and other browsers from Mozilla. This is a free package with open source code, it blocks all JavaScript, Java, Flash and other unsafe plugins unless they are trusted. NoScript can be installed either through the repository Firefox add-ons, or directly from the NoScript website:
NoScript does an excellent job of hiding information about your location and activity from scripts that request such data. The extension hides your digital " fingerprints» from the vast majority of sites on the Internet and provides decent level of anonymity and confidentiality.
Conclusion
Nowadays it is impossible to get complete anonymity on the Internet. This will require a secure VPN server, a variety of browser-based blocking methods, and special setting operating system.
After details of the PRISM intelligence program appeared in the United States and users learned that the state was collecting data from Google and Yahoo!, the number of requests for the anonymous search engine DuckDuckGo increased sharply (from 1.7 million to 3 million). The search engine does not recognize the IP address, does not save cookies and the user’s query history, so it cannot organize answers based on relevance, thus allowing you to see objective results.
A number of other search engines adhere to a similar strategy, which, however, have not gained much popularity. The most famous are Ixquick and Start Page. They all make money from display advertising (in 2011, DuckDuckGo's revenue was $115,000).

Various systems allow you to create temporary mail or simply send messages anonymously. Using “10 Minute Mail” you can open a mailbox for 10 minutes. This, for example, will allow you to register on a new site and avoid further spam. If after 10 minutes you still need access to the mailbox, you can request an extension. "10 Minute Mail" only works for incoming messages.
Hushmail offers a more complex system. Here you need to register, after which you will receive 25 megabytes free space and up to 10 gigabytes for $84.97 per year. There is a separate package for business - for $5.24 per month. Messages are not saved on the server, and it is impossible to recover the password. To prevent the site from “forgetting” you, you need to log in once every 10 days.

Browsers
The most famous browser that provides access to the "closed Internet" is Tor Browser Bundle. It is believed that it is used by those who want to access prohibited (or for other reasons transferred to Tor) sites. But the idea of its creators was to protect users from surveillance and data transfer to advertisers. In standard browsers ( Google Chrome, Internet Explorer, Firefox), anonymity can be achieved by switching to “incognito” mode.
 Anonymous search engine Duckduckgo
Anonymous search engine Duckduckgo Postal service 10 Minute Mail
Postal service 10 Minute Mail Anonymous browser Tor Browser Bundle
Anonymous browser Tor Browser Bundle Spideroak Cloud Storage
Spideroak Cloud Storage Anchorfree service
Anchorfree service CyberGhost service
CyberGhost service

Cloud storage
The SpiderOak project positions itself as the most secure storage. All information reaches the server in encrypted form, and “zero-knowledge” technology is used when processing it. Thus, all information can only be accessed by the account owner. The service earns money using a freemium model: 2 gigabytes can be obtained for free, for additional space you will have to pay $10 per month.

Secure access
There are services that provide secure Internet access via VPN. They use special encryption that protects the browser, blocks malware and allows you to access sites that may not be available in some countries. AnchorFree offers Hotspot Shield connectivity on any device for $30 per year. CyberGhost - similar features are free with a monthly traffic of 1 gigabyte. Advanced features will cost $49 per year. Services also make money from advertising.
It happens in life that you need 100% anonymity when using the Internet through a browser (I’ll do without examples, otherwise tough guys will come to the comments again and accuse me of incitement and threaten me with department “K”). How to make sure that sites on the Internet (for example Google) cannot identify you and record information about any actions in your file?
It happens that you turn on a VPN with “incognito” mode, you don’t log in anywhere, and AdSense suddenly scares you with painfully familiar ads. How does he determine who is who?
To answer this question, let's conduct an experiment. Let's open tabs in four browsers:
- Tor Browser 6.0.2 (based on Mozilla Firefox 45.2.0);
- Safari 9.0 (incognito mode);
- Google Chrome 52.0.2743.82 (incognito mode);
- Mozilla Firefox 46.0.01 (incognito mode).
And let's see what data they can collect about a person. What do we tell the site about ourselves by typing the URL in the address bar?
We provide unique image rendering options (Canvas Fingerprinting)



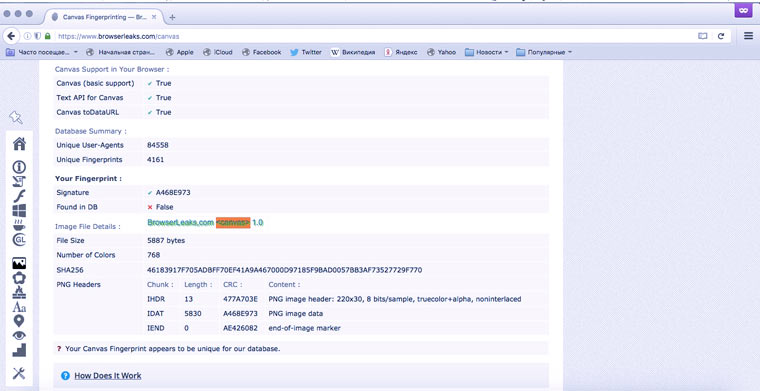
Canvas Fingerprinting is a user identification technology developed about 4 years ago at AddThis. The principle of its operation is based on the fact that when, when loading a page, a picture is drawn (rendered) (usually a single-color block in the background color with invisible text), the browser for this purpose collects a bunch of information about the system: what kind of hardware and graphics drivers, GPU version, OS settings, font information, anti-aliasing mechanisms and many other little things.
Together, this huge variety of details forms a unique characteristic that can distinguish a user's computer/browser combination from all others in the world. For each, it is written as a string similar to DA85E084. There are matches (according to Panopticlick, the average chance of finding a double is 1 in), but in this case, you can supplement them with other opportunities for identification (more on them below).
Tor asks permission to receive Canvas Fingerprinting, and if you are careful and do not give consent, you can keep this information to yourself. But all other browsers surrender their owner without a single peep.
You can read more about this identification method in Wikipedia.
We break through the database of advertising preferences




Many visited sites are now equipped with scripts for determining Canvas Fingerprint. Having received this unique value, one site can ask another for information about the person. For example, linked accounts, friends, IP addresses used and information about advertising preferences. Use the link below to check which systems have your consumer interests linked to Canvas Fingerprinting.
Tor again asked for the same permission as in the first point and, due to my refusal, nothing was found. Safari found me in 3 databases, Chrome in 13, and Firefox in 4. If you exit incognito mode, then in the latter the number of databases increases to 25, since most of them use good old cookies for identification.
We share the IP address and telecom operator




In Tor, you can change your “host country” using the New Identity button. And “incognito” modes do not hide your IP address (for this you must additionally use a proxy or VPN), but share your approximate location and information about your Internet provider with the site owners.
Revealing your city and the time in it (with geolocation services enabled)




On yandex.ru in Tor, without any location permissions, it showed where I was approximately and what time it was. It's the same with other browsers.
Send us your exact coordinates




Tor didn’t even ask permission to determine the coordinates and simply returned zeros. Safari, Chrome and Firefox asked for the standard resolution (as in normal mode) and did not bother to remind me that I was encrypted and should not reveal such data.
Revealing your city and the time in it (with geolocation services disabled)




Then I turned off location services on the Mac and went back to yandex.ru. Tor made the site think that I was in Romania, but left the time in Moscow (due to the mismatch of IP and time zone, it will be possible to ban VPN providers at once in the event of a ban). In other browsers everything remains the same.


The fact is that Yandex does not need GPS (or WPS data from the device) to determine location. After all, he has a “Locator”! Logged into the network via Wi-Fi? The access point is already in the database (see article). Did you give yourself internet from your phone? The cell tower will be rented.
We provide information about language settings




Another sure sign of a VPN lover is that the language does not match the country whose IP he is using. Tor let me down - its language is always English (but it can be changed, but I thought it should change automatically depending on the country). The rest of the settings are the same as in normal mode.
We tell you everything about your browser and system

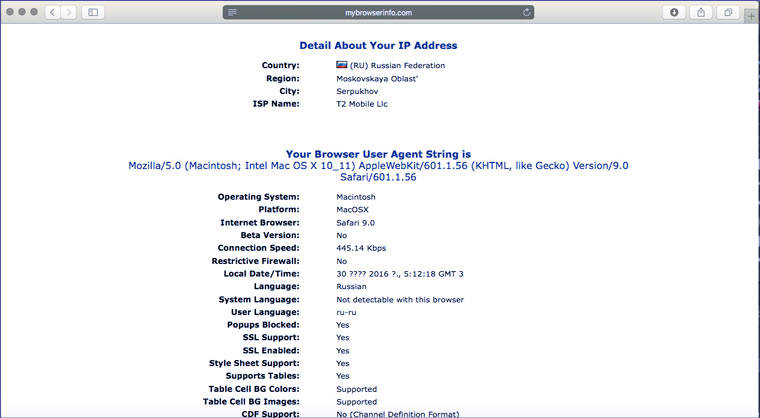


Operating system, connection speed, monitor color characteristics, support different technologies, browser window width, Flash version- a bunch of little things that complement the unique characteristics of the user. Tor manipulates some of this data (Windows 7 example), but other browsers are completely honest.
A person can change the IP, turn on “incognito”, and the script to raise prices will quickly calculate: “Who is this guy who is coming to us with a slow Internet, old version flash and Windows XP for the second time, but now you decide to pretend to be a resident of Seychelles? We’re increasing it by 20%!”
We share a list of installed plugins
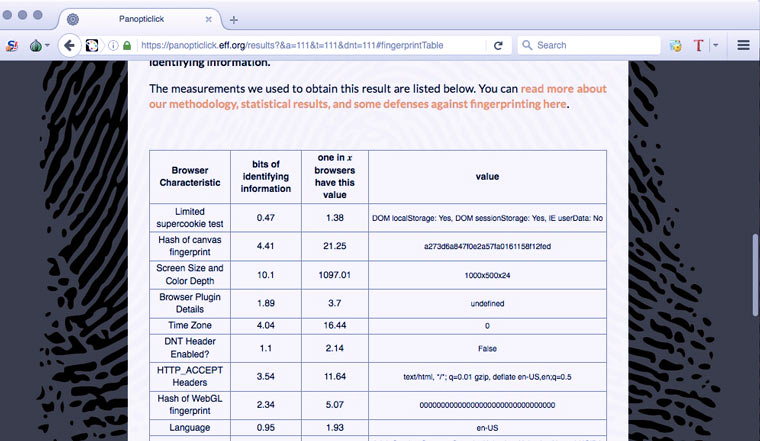



Another characteristic that adds uniqueness to a person is the list of plugins (with version information) installed in his browser. Tor hides them. Other browsers do not.
As you can see, Tor Browser provides good anonymity. But historical facts suggest that if a person does something really serious using the onion network, then he will still be sometimes they find. Everyone probably remembers the illustrative story with the founder Silk Road(drug store) Ross Ulbricht.
And “incognito” modes are only needed to surf on someone else’s computer and not leave traces. In addition to them, you can block JavaScript, this will reduce the number possible ways identification, but many sites will become unusable.
Open the list of fonts installed on the system (=> programs)

In addition to the experiment, I would like to talk about one more interesting function modern browsers. Any site can get a list of fonts installed on the system. Many applications have their own unique fonts, and by using them you can determine a person’s occupation. And based on this, show him advertisements. In Tor and incognito mode this does not work (or the list is too short).
All this is the tip of the iceberg
To protect against the above identification methods, there are special plugins for different browsers. But you shouldn't waste effort installing them. Since they cannot protect against the collection of all possible information.
After all, in the article I showed the simplest and most understandable examples of how browsers collect information about us. But there could be much more of them: flash cookies, Silverlight cookies, time lag behind the standard time (many have at least 0.2-0.8 seconds) - many little things that would be superfluous. After all, the reader already understands that by opening a browser, he communicates a huge amount of information about himself to the world and demonstrates a set of unique characteristics that distinguishes his computer from all others.
What is the threat of all this information gathering?
You need to collect information about the majority of people on the planet for only one purpose - to increase click-through rates advertisements to earn more from it. In principle, this is only beneficial - it is easier to find some goods or services.
More advanced identification methods are useful for stores to collect information about customers. So that a person cannot access the site under a different IP/disabling cookies and remain unrecognized. Language, time, rare font/plugin, monitor characteristics, typical error in search query the way you came - and that’s it! Take off your skates, we recognize you. There is no doubt, this is the same person who placed order #2389 a year ago. With this data, automated marketing systems can sell him more.
Or, naturally, all this can be used by the intelligence services. But who knows how everything works there.
In addition to the sensational opinion on all corners of the Internet about hiding the IP address, there are many other details. By and large, all methods and means of anonymity have the goal of hiding the provider. Through which it is already possible to obtain the physically exact location of the user, having additional information about him (IP, browser fingerprints, logs of his activity in a certain network segment, etc.). And also most methods and means are aimed at maximizing concealment/non-disclosure of this indirect information, according to which later it will be possible to ask the provider of the desired user.
What are the ways to anonymize your online presence?
If we talk about separate units of anonymization (after all, there are also schemes in the form of combining one or another means of anonymity), we can highlight the following:
1) Proxy servers- there are different types, with its own characteristics. Proxy classification under spoiler.
HTTP proxy– works over the http protocol and performs a caching function.
Degrees of anonymity: transparent, distorting, anonymous, elite.
A chain of HTTP proxies can be built only if they support the CONNECT method, with the exception of building a chain using special. programs.
HTTPS proxy(aka CONNECT) – proxies supporting HTTP 1.1, which in turn has two specifications - RFC 2616 and the outdated RFC 2068. They differ in that in special. RFC 2616 documents the CONNECT method.
All of these proxy subtypes have the same capability - they can work using the CONNECT method (in addition to GET/POST).
The difference between the subtypes lies solely in the settings of the proxy server programs:
If the proxy server settings allow connection using the CONNECT method to port 443 (https:// addresses), then this is an HTTPS proxy;
If the proxy server settings allow connection using the CONNECT method to any ports (except 443 and 25), then it is called CONNECT proxy (in ICQ such a proxy is called HTTP proxy);
If the proxy server settings allow connection using the CONNECT method to port 25 ( Post service), then it can be used to send mail and such a proxy is called mail-enabled, or 25 port enabled, or a proxy with the 25th port open.
FTP proxy– works via the ftp protocol and is designed for anonymous management of the site (server). All ftp proxies are anonymous because the FTP protocol does not provide for a proxy.
There are no proxies in the FTP public. It is impossible to build a chain of FTP proxies.
CGI proxy(web anonymizer) is a page on a website where you enter the URL, and it displays the specified page. In this case, the address of this page (indicated in the address field) from the point of view of your computer will be different - something like
http://www.cgi-proxy.com/http/www.your-url.com/path/
From an anonymity point of view, CGI proxies are the same as HTTP proxies. In “mixed” chains, this type of proxy can only be in last place.
SOCKS– this type of proxy has 2 specifications:
Socks 4 works via TCP protocol
Socks 5 Supports TCP, UDP, authentication and remote DNS query. Socks by its nature is truly anonymous (because it works directly with TCP). You can build a chain from proxies of this type. Sox is the most The best way remain anonymous online.
Anonymity Proxy
Everyone knows that when a client interacts with a server, the client sends some information to the server (mostly it is sent by the browser, but the proxy can also add something there “of itself”). This means the name and version of the operating system, the name and version of the browser, browser settings (screen resolution, color depth, java / javascript support, ...), client IP address (if a proxy is used, it is replaced by a proxy server with an IP proxy), used or a proxy server (if a proxy is used, then the client’s IP is an IP proxy - added by the proxy server), if a proxy is used, then your real IP address (added by the proxy server) and much more...
This information is passed in the form of environment variables.
I will only focus on those related to anonymity.
So, If a proxy is not used, then environment variables look like this:
REMOTE_ADDR= Your IP
HTTP_VIA= not defined
HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR= not defined
Transparent proxies do not hide information about the real IP:
REMOTE_ADDR= IP proxy
HTTP_VIA
HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR= real IP
Anonymous proxies(anon) do not hide the fact that a proxy is used, but change the real IP to their own:
REMOTE_ADDR= IP proxy
HTTP_VIA= IP or proxy name (proxy server is used)
HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR= IP proxy
Distorting proxies do not hide the fact that a proxy server is being used. However, the real IP is replaced with another (generally arbitrary, random):
REMOTE_ADDR= IP proxy
HTTP_VIA= IP or proxy name (proxy server is used)
HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR= random IP
Elite proxies(elite, high anon) not only change the IP, but also hide even the fact of using a proxy server:
REMOTE_ADDR= IP proxy
HTTP_VIA= not defined
HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR= not defined
2) VPN services- also work using different protocols, which are offered by providers to choose from.
3) SSH tunnels, were originally created (and still function today) for other purposes, but are also used for anonymization. The principle of operation is quite similar to VPNs, so in this topic all conversations about VPNs will imply them too.
4) Dedicated servers- the main advantage is that the problem of disclosing the request history of the node from which the actions were carried out disappears (as can be the case with VPN/SSH or a proxy).
Is it possible to somehow hide the fact of using Tor from the provider?
Yes, the solution will be almost completely similar to the previous one, only the circuit will go in reverse order And VPN connection“wedges itself” between Tor clients and the network of onion routers. A discussion of the implementation of such a scheme in practice can be found on one of the project documentation pages.

What should you know about I2P and how does this network work?
I2P is a distributed, self-organizing network based on the equality of its participants, characterized by encryption (at what stages it occurs and in what ways), variable intermediaries (hops), IP addresses are not used anywhere. It has its own websites, forums and other services.
In total, when sending a message, four levels of encryption are used (end-to-end, garlic, tunnel, and transport level encryption); before encryption, a small random number of random bytes are automatically added to each network packet to further depersonalize the transmitted information and complicate attempts to analyze the content and block it transmitted network packets.
All traffic is transmitted through tunnels - temporary unidirectional paths passing through a number of nodes, which can be incoming or outgoing. Addressing occurs based on data from the so-called network database NetDb, which is distributed to one degree or another across all I2P clients. NetDb contains:
- RouterInfos- contact details of routers (clients) are used to build tunnels (to simplify, they are cryptographic identifiers of each node);
- LeaseSets- contact information of recipients, used to connect outgoing and incoming tunnels.
The principle of interaction between the nodes of this network.
Stage 1. Node “Kate” builds outgoing tunnels. He turns to NetDb for data about routers and builds a tunnel with their participation.

Stage 2. Boris builds an input tunnel in the same way as an outgoing tunnel. It then publishes its coordinates or so-called "LeaseSet" to NetDb (note here that the LeaseSet is passed through the outbound tunnel).

Stage 3. When “Kate” sends a message to “Boris”, he queries “Boris’s” LeaseSet in NetDb. And it forwards the message through outgoing tunnels to the recipient’s gateway.

It is also worth noting that I2P has the ability to access the Internet through special Outproxy, but they are unofficial and, based on a combination of factors, are even worse than Tor exit nodes. Also, internal sites in the I2P network are accessible from the external Internet through a proxy server. But at these entry and exit gateways there is a high probability of losing some anonymity, so you need to be careful and avoid this if possible.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of an I2P network?
Advantages:
1) High level client anonymity (with any reasonable settings and use).
2) Complete decentralization, which leads to network stability.
3) Data confidentiality: end-to-end encryption between client and recipient.
4) A very high degree of anonymity of the server (when creating a resource), its IP address is not known.
Flaws:
1) Low speed and long response time.
2) “Your own Internet” or partial isolation from the Internet, with the opportunity to get there and an increased likelihood of deanon.
3) Does not save you from attacks via plugins (Java, Flash) and JavaScript, unless you disable them.
What other services/projects are there to ensure anonymity?- Japanese client for Windows for file sharing. The anonymity of the Perfect Dark network is based on the refusal to use direct connections between end clients, the unknown of IP addresses and the complete encryption of everything possible.
The following 3 projects are especially interesting in that their goal - to hide the user - is realized by freeing oneself from provider dependence on an Internet connection, through the construction of wireless networks. After all, then the Internet will become even more self-organized:
- Netsukuku - Networked Electronic Technician Skilled in Ultimate Killing, Utility and Kamikaze Uplinking.
- B.A.T.M.A.N - Better Approach To Mobile Ad-hoc Networking.
Are there any comprehensive solutions to ensure anonymity?
In addition to links and combinations various methods, like Tor+VPN, described above, you can use Linux distributions tailored to these needs. The advantage of such a solution is that they already have most of these combined solutions, all settings are set to ensure maximum quantity boundaries for deanonymizers, all potentially dangerous services and software are cut out, useful ones are installed, some, in addition to the documentation, have pop-up tips that will not let you lose your vigilance late at night.
Based on my experience and that of some other knowledgeable people, I would choose the Whonix distribution, since it contains the latest techniques for ensuring anonymity and security on the network, is constantly evolving and has very flexible configuration for all occasions of life and death. It also has an interesting architecture in the form of two assemblies: Gateway and Workstation, which function in conjunction. The main advantage of this is that if, as a result of the appearance of some 0-day in Tor or the OS itself, through which they try to reveal the hiding Whonix user, then only virtual workstation and the attacker will receive “very valuable” information such as IP 192.168.0.1 and Mac address 02:00:01:01:01:01.

But you have to pay for the presence of such functionality and flexibility in configuration - this determines the complexity of the OS configuration, which is why it is sometimes placed at the bottom of the top operating systems for anonymity.
Easier analogues to set up are the fairly well-known Tails, recommended by Snowden, and Liberte, which can also be successfully used for these purposes and which have a very good arsenal for ensuring anonymity.
Are there any other considerations when achieving anonymity?
Yes, I have. There are a number of rules that it is advisable to adhere to even in an anonymous session (if the goal is to achieve almost complete anonymity, of course) and measures that must be taken before entering this session. Now we will write about them in more detail.
1) When using VPN, Proxy, etc., always set the use in the settings static DNS servers service provider to avoid DNS leaks. Or set the appropriate settings in the browser or firewall.
2) Do not use permanent Tor chains, regularly change output nodes (VPN servers, proxy servers).
3) When using the browser, disable, if possible, all plugins (Java, Flash, some other Adobe tricks) and even JavaScript (if the goal is to completely minimize the risks of deanon), and also disable use of cookies, maintaining history, long-term caching, not allowing sending HTTP User-Agent and HTTP-Referer headers or replacing them (but special browsers are needed for anonymity, most standard ones do not allow such a luxury), using a minimum of browser extensions, etc. In general There is another resource that describes settings for anonymity in various browsers, which is also worth contacting if you wish.
4) When accessing the network in anonymous mode, you should use a “clean”, fully updated OS with the latest stable versions BY. It should be clean - so that it is more difficult to distinguish the “fingerprints” of it, the browser and other software from the average statistical indicators, and updated, so that the likelihood of picking up some kind of malware is reduced and creating certain problems for yourself that jeopardize the work of all means focused on anonymization.
5) Be careful when warnings about the validity of certificates and keys appear to prevent Mitm attacks (eavesdropping on unencrypted traffic).
6) Do not allow any left-wing activity in the anonymous session. For example, if a client from an anonymous session accesses his page on social media. network, then his Internet provider will not know about it. But social the network, despite not seeing the client’s real IP address, knows exactly who is visiting.
7) Do not allow simultaneous connection to the resource via anonymous and open channel(the description of the danger was given above).
8) Try to “obfuscate” all your messages and other products of the author’s intellectual production, since the author can be determined with fairly high accuracy by the jargon, vocabulary and stylistics of speech patterns. And there are already companies that make a whole business out of this, so don’t underestimate this factor.
9) Before connecting to local network or wireless access point, change the MAC address first.
10) Do not use any untrusted or unverified application.
11) It is advisable to provide yourself with a “penultimate frontier”, that is, some kind of intermediate node to your own, through which to conduct all activity (as is done with dedicated servers or implemented in Whonix), so that if all previous obstacles are overcome or the working system is infected third parties gained access to the intermediary blank and did not have any special opportunities to move further in your direction (or these opportunities would be extremely expensive or require a very large amount of time).
First I want to point out that this topic is very extensive, and no matter how I try to convey everything as concisely as possible, but at the same time without missing out on the necessary details and at the same time presenting it as clearly as possible for the average user, this article will still be replete with various technical details and terms, due to which you will have to go to Google. It is also assumed that the reader is familiar with at least the basic aspects of the functioning of most popular services and the global network itself.
What is anonymization anyway?
In addition to the sensational opinion on all corners of the Internet about the concealment IP addresses there are many other details. By and large, all methods and means of anonymity have the goal of hiding the provider. Through which it is already possible to obtain the physically exact location of the user, having additional information about him (IP, browser fingerprints, logs of his activity in a certain network segment, etc.). And also most methods and means are aimed at maximizing concealment/non-disclosure of this indirect information, according to which later it will be possible to ask the provider of the desired user.
What are the ways to anonymize your online presence?
If we talk about separate units of anonymization (after all, there are also schemes in the form of combining one or another means of anonymity), we can highlight the following:
1) Proxy servers- There are different types, with their own characteristics. There is a separate FAQ and other topics on the forum for them;
2) VPN services— they also work using different protocols, which are offered by providers to choose from; see their differences and features below;
3) SSH tunnels, were originally created (and still function today) for other purposes, but are also used for anonymization. The principle of operation is quite similar to VPNs, so in this topic all conversations about VPNs will also include them, but a comparison will be made later;
4) Dedicated servers— the main advantage is that the problem of disclosing the request history of the node from which the actions were carried out disappears (as can be the case with VPN/SSH or a proxy);
5) Great and terrible Tor;
6) - an anonymous, decentralized network operating on top of the Internet, not using IP addressing(see below for details);
7) Other means - anonymous networks, anonymizers etc. Due to their lack of popularity, they have not yet been studied (and therefore do not have a relative guarantee of reliability) by the community, but they are quite promising, see also below for them;
What is worth hiding, or what are de-anonymizing data and methods for obtaining it?
I would like to note right away that all (at least basic) means and methods for hiding data in the list below will be covered in the remaining questions of this FAQ. I would also like to draw your attention to one interesting resource, which is dedicated to the questions of what information we leave about ourselves online when logging into different devices;
1)IP address, or the most popular identifier on the Internet. Makes it possible to find the user’s provider and find out his exact address via the same IP;
2)IP DNS provider, which can be "lost" through a method called ( DNS leaks). It is important to note that this leakage can occur when bonded HTTP/SOCKS4(5 in some cases) + Tor! Therefore, you need to be especially careful here;
3) If most of the traffic goes online for a long time through one node, for example, the same Tor, then you can carry out so-called profiling - attribute certain activity to a certain pseudonym, which can be identified through other channels;
4) Listening to traffic at the exit node or (man in the middle);
5) Simultaneous connection to anonymous and open channels can create troubles in some situations, for example, if the client’s connection is lost, both channels will stop functioning, and the server will be able to determine the desired address by comparing the time the users disconnected (however, this is quite hemorrhagic and far inaccurate method of de-anonymization);
6) Deanonymizing activity in an anonymous session - using public services, especially those that already have information about this user;
7)MAC address who receives WiFi hotspot when connecting to it (or it can be backed up by switches of one of the local networks through which access to the Internet was made);
8) Information from browsers:
- Cookies- This text files with any data (usually unique for each user) stored by an application (often a browser) for various tasks, for example, authentication. It often happens that the client first visited the resource from an open session, the browser saved cookies, and then the client connected from an anonymous session, then the server can match the cookies and figure out the client;
- Flash, Java, Adobe Reader — the first three plugins can generally be distinguished as separate browser-based applications. They can bypass proxies ( DNS leaks), highlight IP ( IP leaks), create your own semblance of long-lived cookies, etc. Also, all three (Flash is especially guilty of this) often serve as an aid for the exploitation of some 0-day or 1-day vulnerabilities, which sometimes allow one to penetrate the system itself;
- JavaScript- executed on the client side, does not have such a wide range of capabilities in terms of deanon, although it can provide accurate information about the OS, type and version of the browser, and also has access to some browser technologies that can also, for example, leak the IP address;
- Browser fingerprint or browser fingerprint— a set of data that the browser constantly provides to the server when working with it, which can form a fairly unique “digital fingerprint” by which it will be possible to find the user even in an anonymous session or later, after leaving it;
How is a VPN different from a proxy?
1) Traffic between the client and the proxy is transmitted in clear text; when using a VPN, encryption is already in progress;
2) Stability - when creating a VPN connection, it is usually constant, disconnections are rarely created, with proxies they occur relatively more often. But it all depends on the provider;
3) In addition to encrypting the connection, VPN provides a more anonymous service in the sense that DNS is used VPN servers service and disclosure of private data such as DNS leak cannot occur, which is no worse than disclosure of an IP address. True, SOCKS5 and SOCKS4a proxies have the same ability to transfer the DNS service to a proxy server;
4) VPN services do not keep logs or only keep logs for very short periods of time and not in detail (at least they say so), most proxy servers do not make such promises;
How effective is a chain of proxy servers?
Rather, it is ineffective if we focus on the ratio of the increase in deanonymization time to the decrease in connection speed from the final resource to the client. In addition, almost all the de-anonymization disadvantages inherent in proxy servers do not disappear when similar chains are built from them. Therefore, we can conclude that it is better not to use this method when achieving anonymity.
The FAQ about proxy servers does not say about SOCKS4a, why is it needed?
This is an intermediate version between SOCKS 4 and 5, in which everything functions similarly to 4, except that SOCKS4a only accepts Domain name instead of the IP address of the resource, it resolves it itself.
Can you tell us more about the features, pros and cons of renting dedicated servers?
A dedicated server is not intended for anonymization, but for hosting applications, services and everything else that the customer deems necessary. It is important to note that the tenant is provided with a separate physical machine, which gives him some guarantee of complete control over this node and creates important advantage for anonymity - confidence that the request history will not leak anywhere.
Considering the above and other points, we can highlight a number of advantages of this tool in terms of anonymization:
1) Setting up an HTTP/SOCKS proxy or SSH/VPN connection of your choice;
2) Control of request history;
3) Saves you from an attack via Flash, Java, JavaScript, if you use a remote browser;
Well, there are also disadvantages:
1) Very expensive method;
2) In some countries, anonymity cannot be provided a priori, because the tenant is required to provide personal information: passport, credit card, etc.;
3) All connections to a dedicated server are logged by its provider, so here a power of attorney of a slightly different type arises;
What protocols do VPNs work through and what features do they have?
It’s better to immediately consider the VPN options that currently exist, that is, what bundles and technologies are offered by providers, unless of course we set the goal of increasing theoretical knowledge network protocols(although there are options using one single protocol, which we will also consider).
SSL (Secure Socket Layer) Secure Sockets Protocol - uses public key data security to verify the identity of the transmitter and recipient. Maintains reliable data transmission through the use of correction codes and secure hash functions. One of the simplest and “low-anonymity” protocols for VPN connections, used mainly by VPN client applications. More often it is part of some kind of deal when creating a VPN connection.
PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) - is used most often, is quite fast, easy to configure, but is considered the least secure compared to its other counterparts. 
L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol) + IPSec(IPSec is often omitted from the name as an auxiliary protocol). L2TP provides transport, and IPSec is responsible for encryption. This connection has stronger encryption than PPTP, is resistant to PPTP vulnerabilities, and also ensures message integrity and party authentication. There are VPNs based on IPSec only or L2TP only, but obviously L2TP + IPSec give more possibilities in protection and anonymization than separately. 

OpenVPN- secure, open, and therefore widespread, allows you to bypass many blocks, but requires a separate software client. Technically, this is not a protocol, but an implementation of VPN technology. conducts all network operations through TCP or UDP transport. It is also possible to work through most proxy servers, including HTTP, SOCKS, NAT And network filters. To ensure the security of the control channel and data flow, OpenVPN uses SSLv3/TLSv1.
SSTP- as secure as OpenVPN, does not require a separate client, but is very limited in platforms: Vista SP1, Win7, Win8. Encapsulates PPP frames V IP datagrams for transmission over the network. To manage the tunnel and transmit PPP data frames, SSTP uses TCP connection(port 443). The SSTP message is encrypted by the channel SSL protocol HTTPS.
Separately, it is worth noting services that provide services such as “DoubleVPN”, when before reaching the desired node, traffic passes through 2 different VPN servers in different regions. Or there is an even tougher solution - “QuadVPN”, when 4 servers are used, which the user can choose himself and arrange in the order he needs.
What are the disadvantages of VPN?
Of course, it is not as anonymous as some other services like Tor, and not only because the algorithm and scheme are different. Also, when using a VPN, in critical situations you will have to rely more on the conscientious performance of the duties of this service (minimal logging, work without traffic backups, etc.).
The next point is that although a VPN hides IP in most cases, it also prevents DNS leak, but there are situations in which this anonymization method will fail. Namely:
1) IP leak via WebRTC - guaranteed to work on Chrome and Mozilla and implemented via regular JavaScript;
2) IP leak via Flash, which initiated a connection to the server and transferred the client’s IP to it, bypassing the VPN (though it doesn’t always work);
Although these cases can be prevented by turning off JS, Flash and Java in your browser;
3) When using client settings by default, when the connection is broken, unlike proxy servers, surfing the network will continue directly, no longer through a virtual channel, that is, it will be a complete disaster;
But this can be avoided by adjusting the routing table, where you can specify only the VPN server gateway as the default default gateway or reconfigure the firewall.
What is the difference between SSH tunnels and VPNs?
An SSH tunnel is nothing more than a connection encrypted using the SSH protocol, where data is encrypted on the client side and decrypted at the recipient ( SSH servers). It is created for remote secure management of the OS, but as already written above, it is also used for anonymization. Supports 2 options: by implementing an HTTP/SOCKS proxy by the application to direct traffic through a local proxy server to an SSH tunnel. Or there is a creation of an almost full-fledged one (one could say something similar, if we take latest versions SSH and OpenSSH) VPN connections. 
VPN was designed to provide secure remote access to resources corporate networks, and therefore the computer connected to the VPN server becomes part of the local network and can use its services. 
That is, apart from the technical minor aspects, the operating principles are similar. And the main difference is that An SSH tunnel is a point-to-point connection, while a VPN connection is a device-to-network connection(although specialists can reconfigure at their discretion).
How does Tor work from the client side?
There are a lot of variations of answers to this question on the Internet, but I want to try to present the basics as simply and concisely as possible, saving the reader from digging through mountains of analytical and complex information.
Tor is a system of routers accessible only to clients of Tor itself, through a chain of which the client connects to the resource he needs. With default settings, the number of nodes is three. uses multi-level encryption. Based on these features, we can briefly describe general scheme delivery of a data packet from the client to the requested resource through 3 nodes (that is, with default settings): the packet is first sequentially encrypted with three keys: first for the third node, then for the second and finally for the first. When the first node receives the packet, it decrypts the “top” layer of the cipher (like peeling an onion) and knows where to send the packet next. The second and third servers do the same. And the transfer of encrypted data between intermediate routers is carried out through SOCKS interfaces, which ensures anonymity coupled with dynamic reconfiguration of routes. And unlike static proxy chains, configuration onion routers can change with almost every new request, which only complicates the deanon. 
What are the advantages and disadvantages of Tor?
Among the advantages it is worth highlighting:
1) One of the highest levels of anonymity (with proper configuration), especially in combination with other methods such as VPN;
2) Easy to use - download, use (you can even do it without any special settings);
Flaws:
1) Relatively low speed, since the traffic goes through a chain of nodes, decryption occurs each time and can pass through another continent altogether;
2) Output traffic can be eavesdropped, and if not used HTTPS, then it’s great to filter for analysis;
3) It may not help if plugins are enabled - Flash, Java and even from JavaScript, but the creators of the project recommend disabling these things;
4) Availability of managing servers;
If a site detects Tor, then there is no way I can access this site anonymously using it?
There are two ways to get to such a site. Using a more sophisticated scheme that de facto makes this visit even more anonymous: a link Tor ⇢ VPN, Can Tor ⇢ Proxy, if you do not need additional anonymity, but only the fact of hiding the use of Tor for the site server, but you must use it in this sequence. It turns out that first the request goes through onion hosts, then through VPN/Proxy, but at the end it looks like it’s just VPN/Proxy(or even a regular connection).
But it is worth noting that the interaction of these connections causes heated discussions on forums; here is the section about Tor and VPN on the onion project website. 
Or you can use the so-called bridges (bridges) are nodes that are not listed in the central Tor’a directory; you can see how to configure them.
Is it possible to somehow hide the fact of using Tor from the provider?
Yes, the solution will be almost completely similar to the previous one, only the scheme will go in the reverse order and the VPN connection will be “wedged” between Tor’a clients and the network of onion routers. A discussion of the implementation of such a scheme in practice can be found on one of the project documentation pages. 
What should you know about I2P and how does this network work?
I2P- a distributed, self-organizing network based on the equality of its participants, characterized by encryption (at what stages it occurs and in what ways), intermediary variables (hops), not used anywhere IP addresses. It has its own websites, forums and other services.
In total, four levels of encryption are used when sending a message ( through, garlic, tunnel, and transport layer encryption), before encryption, a small random number of random bytes are automatically added to each network packet to further anonymize the transmitted information and complicate attempts to analyze the content and block transmitted network packets.
All traffic is carried through tunnels - temporary unidirectional paths passing through a number of nodes, which can be incoming or outgoing. Addressing occurs based on data from the so-called network database NetDb, which is distributed to one degree or another across all clients I2P. NetDb contains:
- RouterInfos— contact details of routers (clients) are used to build tunnels (to simplify, they are cryptographic identifiers of each node);
- LeaseSets— contact details of recipients, used to connect outgoing and incoming tunnels.
The principle of interaction between the nodes of this network.
Stage 1. Node “Kate” builds outgoing tunnels. He turns to NetDb for data about routers and builds a tunnel with their participation. 
Stage 2. Boris builds an input tunnel in the same way as an outgoing tunnel. It then publishes its coordinates or so-called "LeaseSet" to NetDb (note here that the LeaseSet is passed through the outbound tunnel). 
Stage 3. When “Kate” sends a message to “Boris”, he queries “Boris’s” LeaseSet in NetDb. And it forwards the message through outgoing tunnels to the recipient’s gateway. 
It is also worth noting that I2P has the ability to access the Internet through special Outproxy, but they are unofficial and, based on a combination of factors, are even worse than Tor exit nodes. Also, internal sites in the I2P network are accessible from the external Internet through a proxy server. But at these entry and exit gateways there is a high probability of losing some anonymity, so you need to be careful and avoid this if possible.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of an I2P network?
Advantages:
1) High level of client anonymity (with any reasonable settings and use);
2) Complete decentralization, which leads to network stability;
3) Data confidentiality: end-to-end encryption between client and recipient;
4) A very high degree of anonymity of the server (when creating a resource), its IP address is not known;
Flaws:
1) Low speed and long response time;
2) “Your own Internet” or partial isolation from the Internet, with the opportunity to get there and an increased likelihood of deanon;
3) Does not protect against attacks via plugins ( Java, Flash) And JavaScript, if you do not disable them;
What other services/projects are there to ensure anonymity?
- Freenet - peer-to-peer network distributed data storage;
- GNUnet is a coordinated set of software for peer-to-peer connections that does not require servers;
- JAP - John Donym, based on Tor;
- — cross-platform software for serverless email exchange, instant messages and files using an encrypted peer-to-peer F2F (friend-to-friend) network;
- Perfect Dark is a Japanese client for Windows for file sharing. Network anonymity Perfect Dark is based on the refusal to use direct connections between end clients, the unknown IP addresses and complete encryption of everything possible;
The next 3 projects are especially interesting in that their goal is to hide the user by freeing themselves from provider dependence on an Internet connection, through the construction of wireless networks. After all, then the Internet will become even more self-organized:
- Netsukuku - Networked Electronic Technician Skilled in Ultimate Killing, Utility and Kamikaze Uplinking;
- B.A.T.M.A.N - Better Approach To Mobile Ad-hoc Networking;
Are there any comprehensive solutions to ensure anonymity?
In addition to bundles and combinations of various methods, like Tor+VPN, described above, you can use Linux distributions tailored to these needs. The advantage of such a solution is that they already have most of these combined solutions, all settings are set to provide the maximum number of boundaries for de-anonymizers, all potentially dangerous services and software are cut out, useful ones are installed, some, in addition to the documentation, have pop-up tips that will not let later users in the evening to lose vigilance.
Based on my experience and that of some other knowledgeable people, I would choose the Whonix distribution, since it contains the latest techniques for ensuring anonymity and security on the network, is constantly evolving and has very flexible configuration for all occasions of life and death. It also has an interesting architecture in the form of two assemblies: Gateway And Workstation, which function in conjunction. The main advantage of this is that if any 0-day in Tor or the OS itself, through which they will try to reveal the hiding user Whonix, then only the virtual Workstation will be “deanonymized” and the attacker will receive “very valuable” information like IP 192.168.0.1 And Mac address 02:00:01:01:01:01.
But you have to pay for the presence of such functionality and flexibility in configuration - this determines the complexity of the OS configuration, which is why it is sometimes placed at the bottom of the top operating systems for anonymity.
Easier analogues to set up are the fairly well-known one recommended by Snowden and Liberte, which can also be successfully used for these purposes and which have a very good arsenal for ensuring anonymity.
Are there any other considerations when achieving anonymity?
Yes, I have. There are a number of rules that it is advisable to adhere to even in an anonymous session (if the goal is to achieve almost complete anonymity, of course) and measures that must be taken before entering this session. Now we will write about them in more detail.
1) When using VPN, Proxy etc. Always set the settings to use static DNS servers service provider to avoid DNS leaks. Or set the appropriate settings in the browser or firewall;
2) Do not use permanent Tor chains, regularly change output nodes (VPN servers, proxy servers);
3) When using the browser, disable, if possible, all plugins (Java, Flash, some other Adobe crafts) and even JavaScript (if the goal is to completely minimize the risks of deanon), and also disable the use of cookies, history keeping, long-term caching, do not allow send HTTP headers User-Agent And HTTP-Referer or replace them (but special browsers are needed for anonymity; most standard ones do not allow such a luxury), use a minimum of browser extensions, etc. In general, there is another resource that describes settings for anonymity in various browsers, which is also worth contacting if you wish;
4) When accessing the network in anonymous mode, you should use a “clean”, fully updated OS with the latest stable software versions. It should be clean - so that it is more difficult to distinguish the “fingerprints” of it, the browser and other software from the average statistical indicators, and updated, so that the likelihood of picking up some kind of malware is reduced and creating certain problems for yourself that jeopardize the work of all means focused on anonymization;
5) Be careful when warnings about the validity of certificates and keys appear to prevent Mitm attacks(eavesdropping on unencrypted traffic);
6) Do not allow any left-wing activity in the anonymous session. For example, if a client from an anonymous session accesses his page on social media. network, then his Internet provider will not know about it. But social the network, despite not seeing the client’s real IP address, knows exactly who is logged in;
7) Do not allow simultaneous connection to the resource via an anonymous and open channel (the danger was described above);
8) Try to “obfuscate” all your messages and other products of the author’s intellectual production, since the author can be determined with fairly high accuracy by the jargon, vocabulary and stylistics of speech patterns. And there are already companies that make a whole business out of this, so don’t underestimate this factor;
9) Before connecting to a local network or wireless access point, first change MAC address;
10) Do not use any untrusted or unverified application;
11) It is advisable to provide yourself with a “penultimate frontier”, that is, some kind of intermediate node to your own, through which to conduct all activity (as is done with dedicated servers or implemented in Whonix), so that if all previous obstacles are overcome or the working system is infected, third parties will gain access to the intermediary blank and will not have any special opportunities to move further in your direction (or these opportunities would be very expensive or require a very large amount of time);
We can summarize with a very obvious conclusion: the more anonymous/secure the technology or method, the less speed/convenience it will be when using it. But sometimes it is better to lose a couple of minutes waiting or spend a little more effort and time using complex techniques than to then lose a significantly larger amount of time and other resources from the consequences that may occur due to the decision to relax somewhere.
Last updated by at January 18, 2016.